Thermodynamics
The study of energy transfer and transformation that occur in matter is called thermodynamics.
Laws of thermodynamics
- First law of thermodynamics : states that the total amount of energy in the universe is constant, and that it can neither be increased or decreased. Energy can neither be created or destroyed.
- Second law of thermodynamics : states that for any process to occur, there needs to be a decrease in free energy and increase in chaos or randomness.
What is entropy?
Entropy is central to the second law of thermodynamics, which states that the entropy of an isolated system left to spontaneous evolution cannot decrease with time. As a result, isolated systems evolve toward thermodynamic equilibrium, where the entropy is highest.
What is enthalpy?
Enthalpy is the sum of a thermodynamic system’s internal energy and the product of it’s pressure and volume.
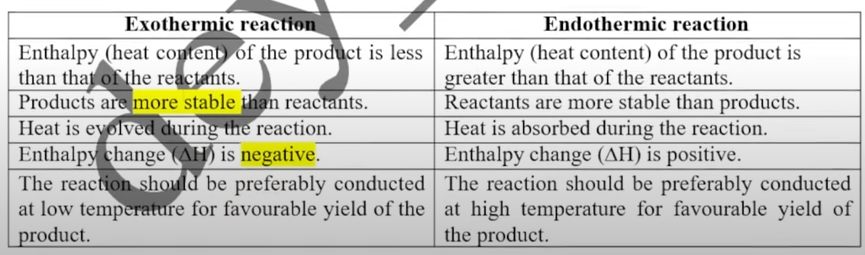
Endergonic vs Exergonic Reactions

Exothermic vs Endothermic reactions
Concept of and it’s relation to standard free energy
is the equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction and is the value of it’s reaction quotient at chemical equilibrium.
==If then the concentration of products is greater than that of the reactants and forward reaction is favoured.==
==If then the concentration of products is lesser than that of the reactants and reverse reaction is favoured.
==If then neither forward nor backward reaction is favoured.
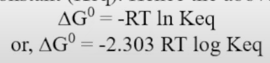
Here is the standard free energy (or Gibbs free energy) Q is the reaction quotient is the equilibrium constant
Spontaneity
The tendency of a process to occur naturally is called it’s spontaneity. It is related to entropy.
Entropy of a system is a state function and only depends on the initial and last state. It is denoted by S.
The change in disorder is denoted by

ATP as an energy currency
ATP(adenosine triphosphate) consists of a purine base adenine, a pentose sugar ribosome and three molecules of phosphoric acids.
In ATP, the last phosphate group is linked with ADP by a special bond, known as "Energy rich bond" When the last phosphate group of ATP is released, a large amount of energy is released.
It is given by the following reaction:
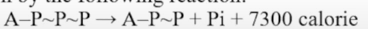

Energy yielding and energy consuming reactions.
Reactions which produce energy are called energy yielding Reactions which consume energy are called energy consuming
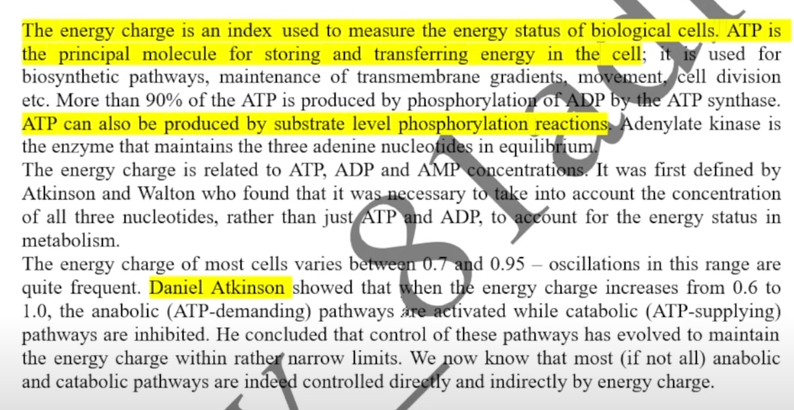
Concept of energy charge
The energy charge is an index to measure the energy level of biological cells.
Photosynthesis phases



